The scientific community recently was abuzz as the existence of gravitational waves has been confirmed. Albert Einstein predicted the existence of gravitation waves 100 years ago with his general theory of relativity. Do you still remember E=mc2? You better!
Gravitation waves are ripples in the spacetime continuum that provide scientists with details about this history of the cosmos. They are produced by cosmic events such as the combining of two black holes.
While gravitational waves were predicted in 1915, a scheme for measuring them was not proposed until the 1980s. Leading scientists, including noted physicist Richard P. Feynman, suggested using a technique called laser interferometry.
This basically combines several lasers sources into one multi-frequency beam of light. A series of high-precision mirrors and sensors look for differences in the reflected beam of light to monitor for gravity waves. This overly simplistic explanation illustrates the need for finely tuned interferometers to measure the gravity waves.
The recent gravity wave detections were observed at twin Laser Interferometer Gravitational-wave Observatory (LIGO) detectors in the United States. The LIGO instrumentation was recently upgraded to increase the sensitivity and range of the system.
High precision Data Acquisition Modules (DAQ Modules) were used to measure the interferometer signals. The DAQ Modules have two requirements for high precision operation: fast data rates and good signal integrity.
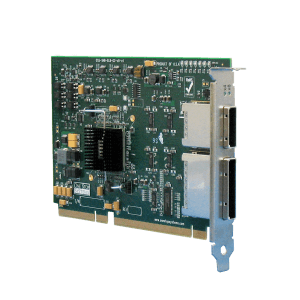
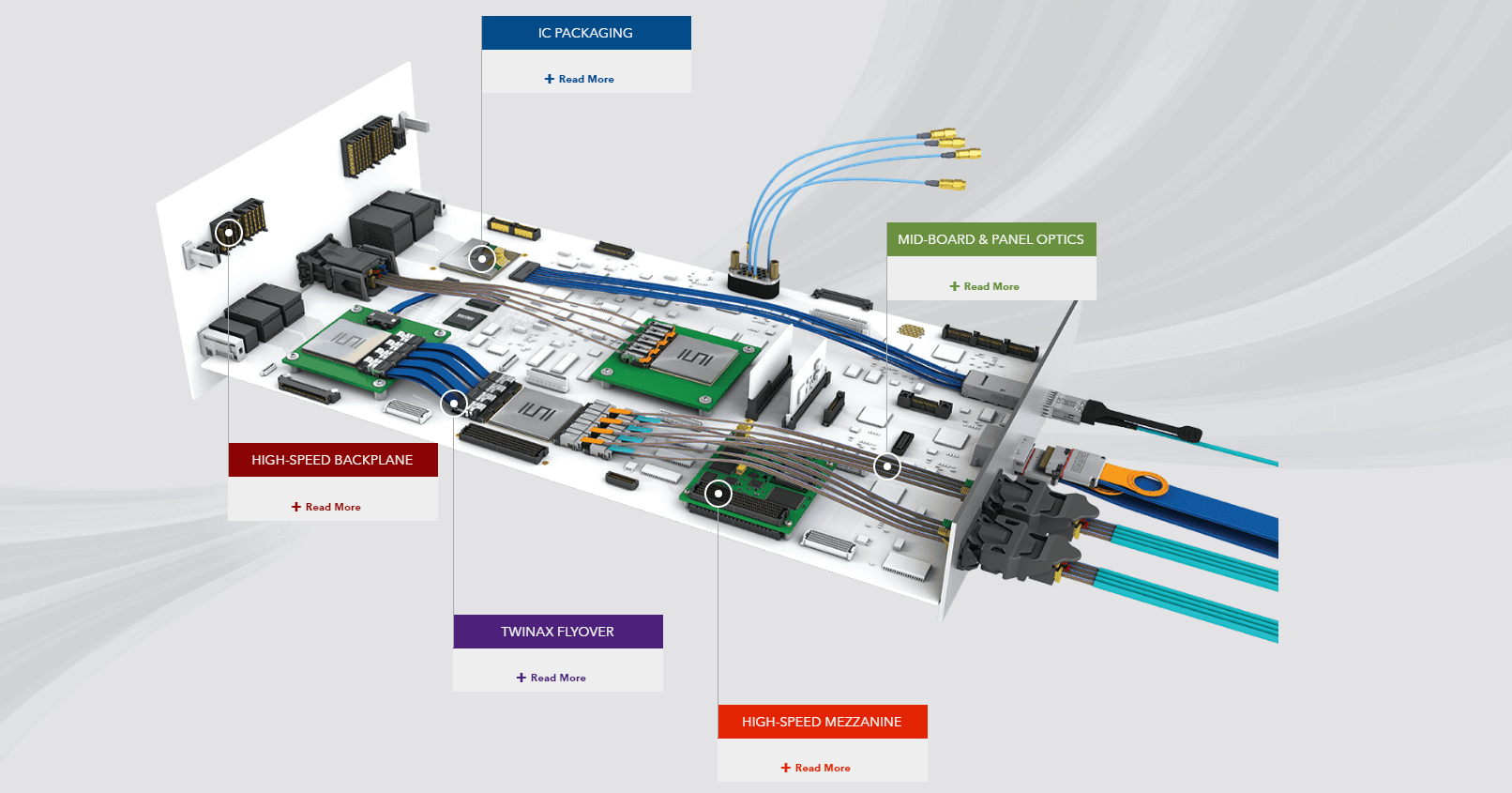
One Stop Systems provide a simple bus interface with thorough bandwidth to support the data acquisition needs of the LIGO system. LIGO servers contain Cable Host Adapters at the PCIe host. The LIGO DAQ Modules use PCIe Expansion Boards as PCIe endpoints.
Connecting these PCIe solutions together may seem standard, but the LIGO servers were placed long distances (up to 120m) away from the DAQ modules. The physical separation helped reduce vibration noise from affecting the DAQ Modules. Electrical isolation via rugged, high-speed active optical cable assembles (AOCs) improved signal integrity within the LIGO system.

One Stop Systems partnered with Samtec to use various PCIEO series AOCs in the LIGO system. Features of Samtec PCIEO AOCs include:
- iPass™ form factor (iPass™ is a trademark of Molex Incorporated.)
- Gen 3 speed up to 100 meters
- Lightweight 3 mm diameter cable
- Supports PCIe® auxiliary signaling (CPWRON, CPERST#, CPRSNT#, CWAKE#)
- Male or female MTP optical connector termination available
- Backwards compatible
- Form factors x4 and x8 standard (including x4 to x8 adaptors)
Please send enquiries of pricing, support and technical detail on these any Samtec optical products to [email protected]. For more information on Samtec’s optical products, please download the following resources: