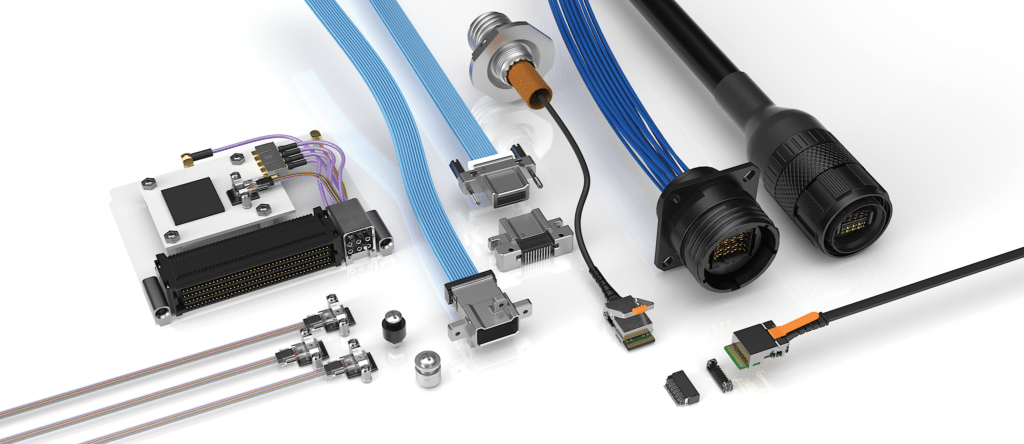
In the world of modern warfare, electronic warfare (EW) has emerged as a pivotal domain, enabling the manipulation of the electromagnetic spectrum for strategic advantage. At the heart of effective electronic warfare systems lies a critical yet often overlooked component: the interconnects.
Samtec delivers Sudden Service® solutions that are engineered to meet the stringent quality, production, and compliance requirements of many standard and application-specific military and aerospace applications. Our extensive MIL standard and Severe Environment Testing initiatives, along with an extremely flexible portfolio of high-performance interconnects, enable quick-turn and cost-effective solutions that provide the ultimate in performance and reliability.
Across the Spectrum and Multi-Domain Electronic Warfare
Multi-Domain includes both physical and non-physical areas. Land, air, maritime, and space are easily identified as physical locations. Cyberspace, the information environment, and the electromagnetic spectrum travel across and around the physical domains. Each warfighter may have a focus in one physical domain but the non-physical now affects them all.
Within each non-physical domain, there is a spectrum of electromagnetic frequencies that can be used. At the bottom of the article is a list of uses and ranges of frequency we find in the electromagnetic spectrum. Included are applications across the warfighter’s landscape, enhancing communication, intelligence, surveillance, reconnaissance, targeting, and defensive capabilities.

Groups like Modular Open Systems Approach (MOSA) and Sensor Open Systems Architecture (SOSA) are helping to align technologies across domains and within the US Department of Defence (DOD). These organizations are utilizing embedded standards designed to work in harsh environments like many created by VMEbus International Trade Association (VITA). Samtec has quite the offering of interconnects that are designed into these standards bodies.
The Right Electronic Ammunition Delivery Sytems
Selecting the appropriate connector for an EW system bears striking similarities to choosing the right weapon on the battlefield. Just as a weapon’s type and caliber must align with the tactical situation, connectors must match the system’s technical requirements. Just as a soldier’s weapon is an extension of their capabilities, connectors are essential for efficient data exchange and performance in EW operations.
Durability
Durability may include reliability, maintainability, and portability while keeping size, weight, and power (SWaP) in mind. These connectors are deployed in challenging environments, including high temperatures, extreme vibrations, electromagnetic interference, and even combat situations.
Stability
Stability in the transmission lines ensures that signals are transmitted with minimal distortion, noise, or loss. Maintaining signal integrity is essential for accurate data transmission and reception in EW operations. This includes processing and exchanging large amounts of data in real time. Interconnects facilitate the rapid and reliable transfer of data between different components of the system.
Electronic Warfare
Interconnects across the spectrum, domain, or system architecture need durable and stable solutions. Samtec is proud to be involved with many standards bodies to bring commercial-off-the-shelf (COTS) products to market as well as support the most demanding designs for signal integrity.
Samtec is also pleased to partner with industry leaders in promoting educational opportunities around EW like the Association of Old Crows and their Podcast where they discuss the challenges facing the warfighter. Listen in as they talk with Samtec customers, partners, and other industry leaders related to electromagnetic spectrum operations (EMSO).
For specific design requirement help please reach out to our experts at [email protected] for all of your EW interconnect needs.
Frequency Ranges and Applications
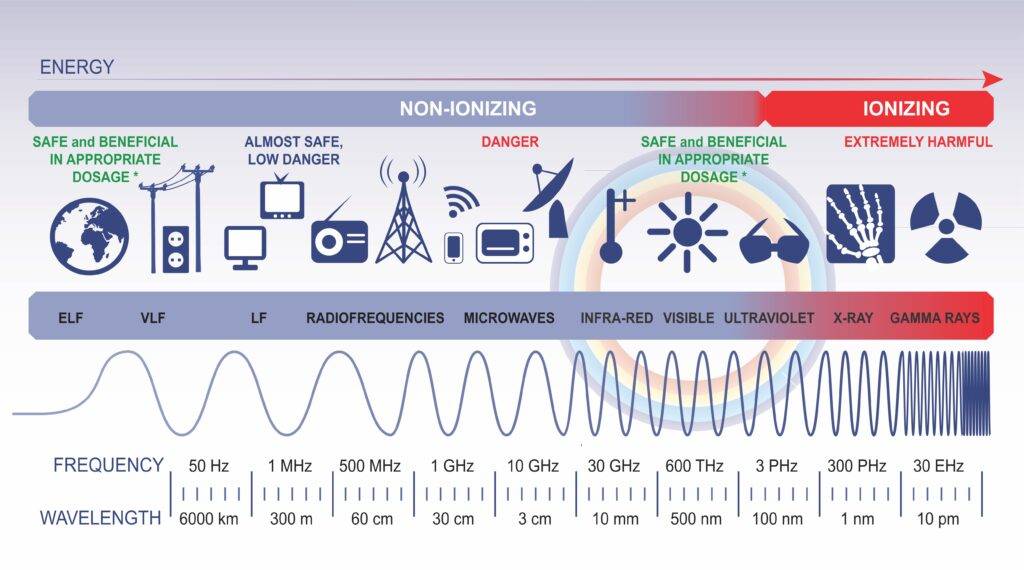
Various electromagnetic waves used across different domains:
- Radio Waves (3 kHz – 300 GHz): Employed for long-range communication, data transmission, and navigation (e.g., HF, VHF, UHF bands).
- Microwaves (300 MHz – 300 GHz): Used for radar systems, targeting, and satellite communication (e.g., S-band, X-band, Ku-band).
- Infrared (IR) Waves (1 THz – 1,000 THz): Utilized in thermal imaging, night vision, and laser targeting systems.
- Visible Light (430 THz – 750 THz): Applied for signaling, marking, and optical communication in tactical scenarios.
- Ultraviolet (UV) Waves (10 PHz – 100 PHz): Used for identifying chemical and biological agents and detecting counterfeit items.
- X-rays (30 EHz – 30 ZHz) and Gamma Rays (300 EHz – 300 ZHz): Applied in imaging for security checks, identifying concealed objects, and non-destructive testing.
- Terahertz Waves (0.1 THz – 10 THz): Used in imaging, spectroscopy, and concealed object detection in various security applications.
- Electromagnetic Pulses (EMP): Created by high-energy sources and used to disrupt electronics and communication systems.
- Magnetometer Waves: Detect magnetic anomalies for landmine detection and unexploded ordnance clearance.





Leave a Reply