Vision systems are playing a key role in the future of automotive design. Understanding and reacting to the hazards found on our roads has historically been a burden that belongs to the driver, but modern vehicles are playing a greater role than ever in keeping us safe.
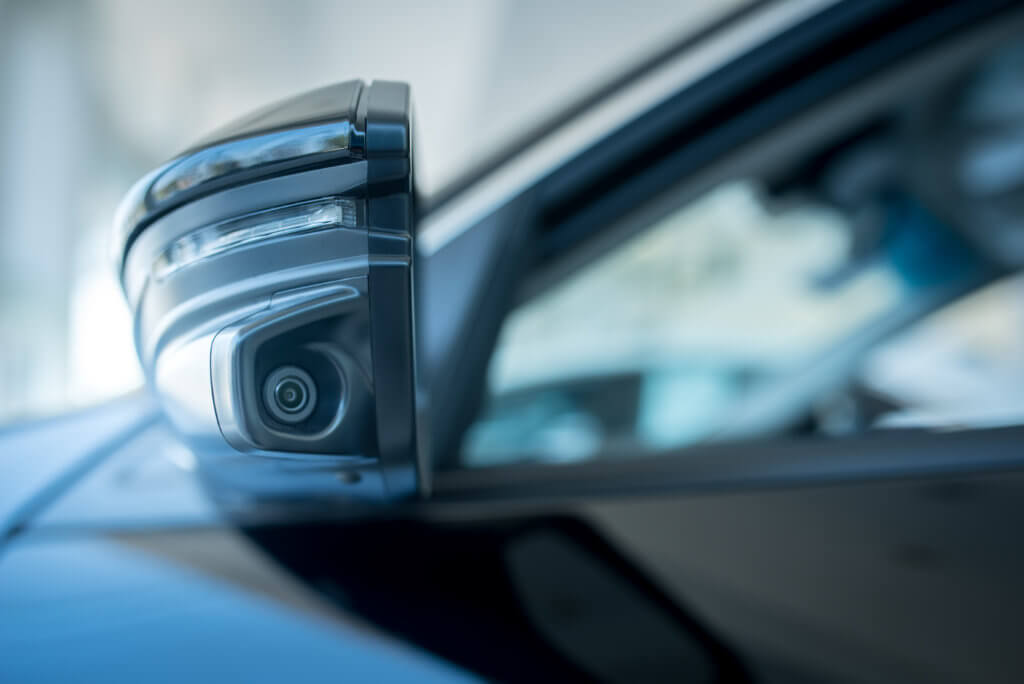

Vision systems, whether visible light cameras or advanced detection systems such as LIDAR (light detecting and ranging) and proximity sensors are tools that can be employed to improve our situational awareness. The first vision systems mounted to vehicles – especially family cars – were reversing cameras that improved safety when maneuvering in confined spaces. However, the reduced size and greater capabilities of modern cameras and sensors make them key to the latest smart vehicles.
The simplest use of cameras is to provide an all-around view of the vehicle, especially in blind spots. The latest cameras are small and light enough to be fixed in wing mirrors and bodywork. Integrating these into the infotainment system requires connectors that are compact and lightweight. They need to be able to withstand both the vibration found in automotive applications and the tough conditions found on our roads.
This high-definition picture is being used to great effect in the latest advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). Combined with advanced in-car displays, these systems are being used to improve the driver’s situational awareness by highlighting important information, such as the current speed limit and distance to other traffic.
Augmented Reality
This is being further integrated into augmented reality displays. Using the information gathered from these vision systems, the driver is presented with a view of the real world, over which is projected the information that will keep them safe. This can include the edges of the road surface and nearby traffic along with important navigation information, all of which can provide the driver with advanced knowledge of any potential hazards.
The most advanced use of vision systems is in the field of autonomous or driverless vehicles. Human drivers develop skills based upon learning and experience until they become entirely automatic. For machines to perform the same tasks requires high levels of computing power along with an accurate picture of the world around them. Lives may depend on their quick reactions.
Autonomous vehicles use radar and LIDAR along with conventional cameras to create a 3-dimensional image of their surroundings. The on-board AI (artificial intelligence) then interprets this image in real-time and uses it to react to hazards immediately. The AI must be able to differentiate between static and moving hazards, and act accordingly.

The Data Needs of Automotive Vision Systems
These requirements place great demands on the infrastructure built into the vehicle. These modern cameras and sensors generate huge amounts of data, which must be transmitted without losing definition. The connectors used to integrate these sensors into the in-car systems must be capable of conducting this stream of information accurately, even in the demanding conditions of the automotive world.
Samtec manufactures a range of high-speed connectors that are specifically designed to provide superior board-to-board and board-to-wire solutions in harsh conditions. Samtec has created the Severe Environment Testing (SET) program, in which connectors are tested far beyond conventional standards for service life, vibration, shock and temperature cycling. Certified to IATF 16949, ISO 14001 and ISO 9001, and with vertically integrated manufacturing processes, Samtec has the expertise to help solve the most demanding imaging challenges.
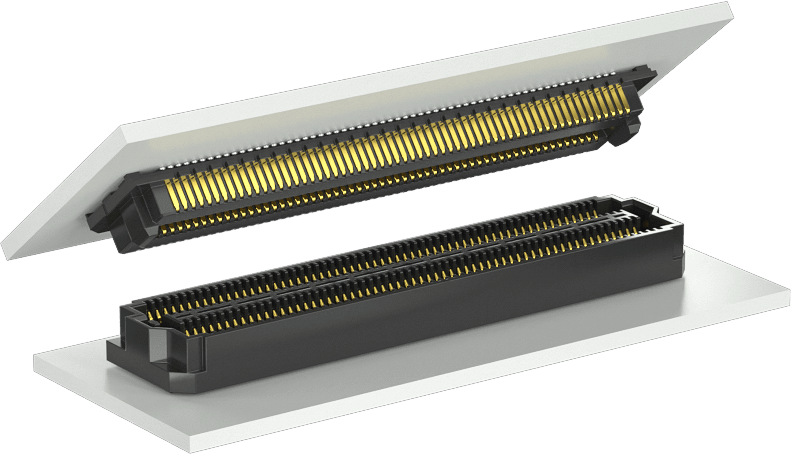
Take a look at the latest Automotive applications page to learn more about how Samtec’s products, testing and manufacturing facilities make us your ideal partner for connecting the latest vision systems.

Leave a Reply