This summer my family and I decided to invest in not only one, but two Electric Bikes.
At first, I was not fully on board about investing in this purchase. But then I started remembering the fun bike rides I used to go on and I began feeling nostalgic. I rode all kinds of places on my bike as a kid, of course, within a reasonable distance. I used to explore nature, my community, and my bike was a semi-easy means of transportation to catch up with my friends. In the early 2000’s Electric bikes certainly would have helped me go longer distances and assist on those back road PA hills like never before.

History of Electric Bikes
Electric bikes (e-bikes) have revolutionized the way we experience cycling, offering a harmonious blend of human effort and motorized assistance. In the ever-evolving landscape of transportation, the electric bike, has emerged as a game-changer, combining the efficiency of a bicycle with the power of electricity.
According to A brief history of Electric Bikes, the history of electric bikes surprisingly goes back to the 19th century, when inventors and engineers were trying to convert safety bicycles into powered bicycles.
The biggest issue during this time period were the batteries, as they were bulky and very heavy. However, the weight problem was resolved in 1991 with the invention of the lithium-ion battery. As a result, electrical bikes looked almost identical to a classic non-assisted bike with the main difference being the ease of traveling up hills.
The COVID-19 pandemic also induced a massive “bike boom” and as a result accelerated the transition to electric bicycles. The switch generated new opportunities for many people, giving them the confidence to go out longer and more often than they would have on a traditional bike.
The Bells and Whistles of Electric Bikes
Electric bikes (e-bikes) have undergone a remarkable transformation over the decades, and thanks in part to the incorporation of advanced sensors. The two primary sensors responsible for this dynamic interaction are the torque sensor and the cadence sensor.
Torque Sensor
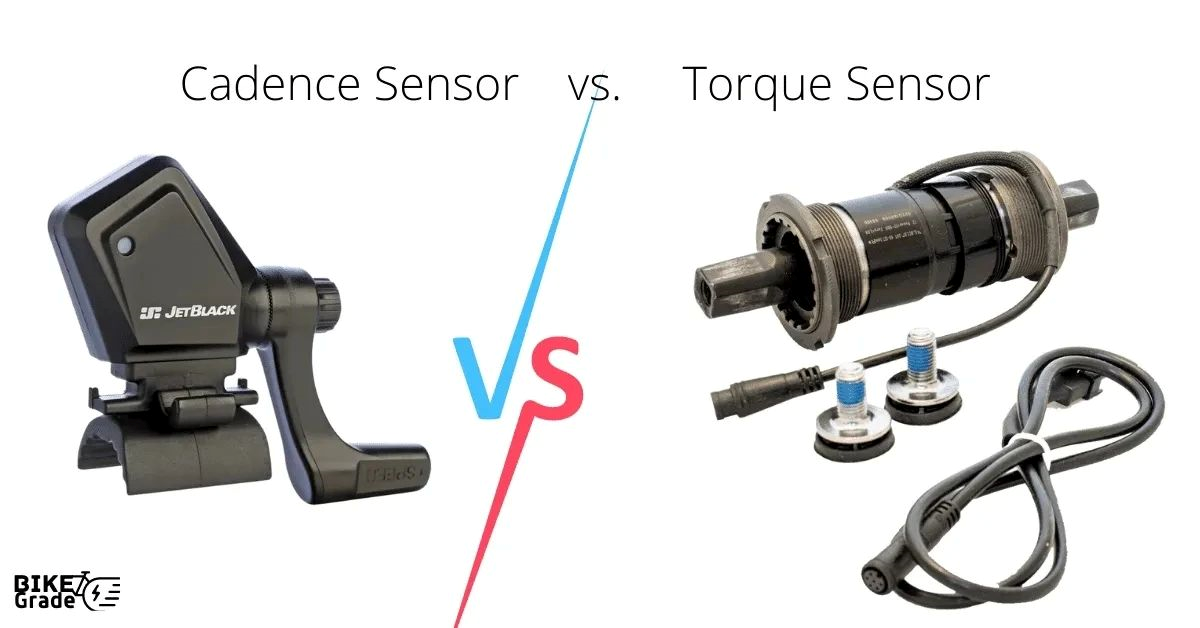
At the heart of an e-bike’s torque sensor is the ability to measure the force applied by the rider on the pedals. Torque, in this context, refers to the twisting force that causes rotation. The torque sensor is typically integrated into the bottom bracket or crankset area of the bike. It measures the force applied by the rider’s legs and translates it into data that the e-bike’s motor controller can interpret.
Cadence Sensor
The cadence sensor, as the name suggests, tracks the revolutions of the pedals. Cadence refers to the rate at which a cyclist pedals and how fast they are turning the pedals. This sensor is often placed on the bike’s crank or chainring. The cadence sensor provides important information about the rider’s pedaling rhythm and speed.
Other Electric Bike sensor technology includes:
- Battery Level sensor
- Brake sensor
- Incline and Tilt sensor
- Motor Efficiency
- Smart Integration of Smart phones
- Regenerative braking extending battery life
- Lightweight design with advanced materials of carbon fiber and aluminum
Above all these sensors gather data and information to enable precise control and intelligent decision-making. They provide real-time feedback to various components, ensuring that the electric bike (e-bike) signals operates smoothly and optimally.
Connectors and Cables
The history of Electric bicycles is a journey marked by innovation, adaptation, and the pursuit of efficient mobility. Behind the scenes of a seamless electric bike ride lies a sophisticated network of connectors and cables. As the e-bike industry continues to evolve, sensor and signal technology will remain at the forefront, providing riders with enhanced experiences on two wheels.
I can not wait for more adventures with my family on our E Bikes – Any tips and tricks send my my way!



Leave a Reply