Embedded computing – What is that?
I ask myself that question because of a class I am taking at San Jose State University – Microprocessor-Based System Design. Embedded systems are everywhere, from your mobile devices, to drones, vehicles, and robots. However, in my course we focus on robotics ARM processors as ARM processors account for approximately 90% of all embedded 32-bit RISC processors.
Some facts about ARM processors include:
- As of 2005, 98% of the more than one billion mobile phones sold each year used ARM processors
- In 2010 alone, 6.1 billion ARM-based processors represented:
- 95% of smartphones
- 35% of digital television and set-top boxes
- 10% of mobile computers
- As of 2014, over 50 billion ARM processors have been produced
As a robotics enthusiast myself, I am very excited about this course. I can’t wait to learn more about ARM processors! But, what makes “embedded computing” different? There are quite a bit of differences between embedded computing, personal computing, fog computing, and edge computing.
Embedded Computing Defined
When comparing embedded computing with personal computing, the key difference is that an embedded device can operate without human interaction. A computer is a combination of hardware and software resources which integrate and provides various functionalities to the user.
An embedded device is a part of an integrated system which is formed as an combination of computer hardware and software for a specific function and which can operate without human interaction.
Edge computing and Fog computing are similar in the sense that they both process data, however, they differ in how they process data. Edge computing helps devices to get faster results by processing the data simultaneously received from the devices.
Fog computing helps in filtering important information from the massive amount of data collected from the device and saves it in the cloud by sending the filtered data.
Embedded Computing Applications
Where does embedded computing play a role in all of this? Embedded systems also process data. Embedded systems use the communication ports to transmit the data between the processor and peripheral devices – often, other embedded systems – using communication protocol. The processor interprets this data with the help of minimal software stored on the memory.
However, when comparing embedded computing with personal, fog, and edge computing, embedded systems can do a lot more. Characteristics of embedded systems include:
- It consists of hardware, software and firmware
- Can be embedded in a larger system to perform a specific function
- Can be either microprocessor-based or microcontroller-based
- Are often used for sensing and real-time computing in internet of things (IoT) devices.
- Can vary in complexity and in function, which affects the type of software, firmware, and hardware they use.
Embedded Computing – Samtec’s Angle
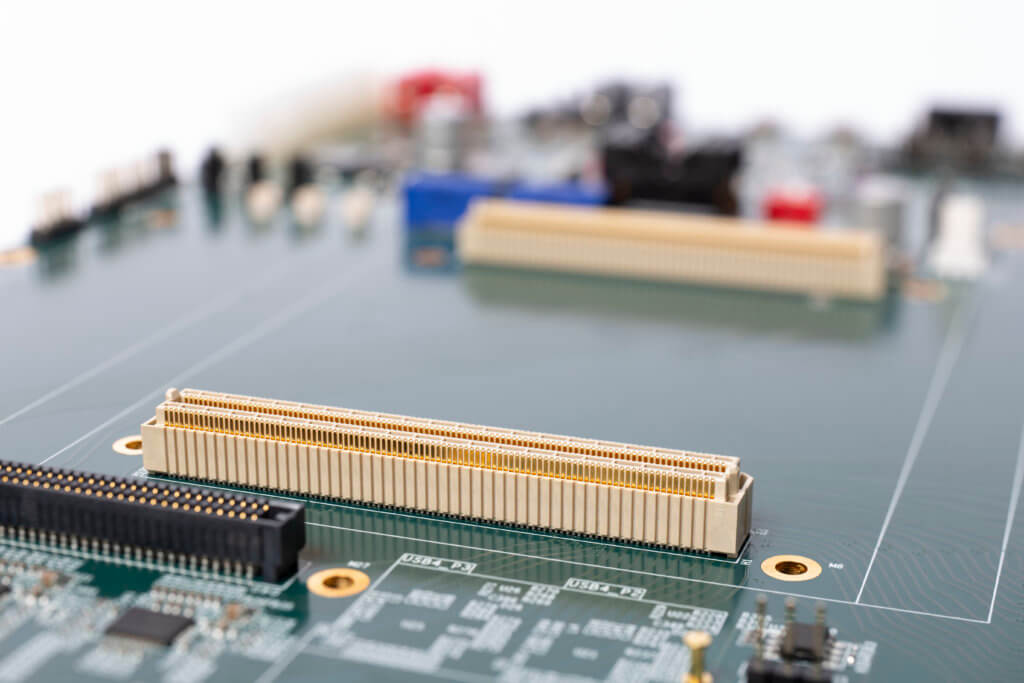
Samtec is a big player in embedded computing from PC/104™ solutions, to exceeding high-speed performance through the development COM-HPC® products, to the open standards and open markets through VITA Technologies.
Samtec’s PC/104 products has proven to be simple elegant in design, while providing rugged performance on land and space. PC/104 technology merges the successes of past technologies with the confidence of future innovations. Samtec offers PC/104™ Standard, PC/104-Plus™, and PCI/104-Express™.

Samtec’s COM-HPC interconnect exceed the demand for high-speed performance in embedded computers. COM-HPC coexists with the COM Express specification to provide the scalability and enhanced performance for next-gen embedded system design.
The COM-HPC specification defines two different module types. COM-HPC server modules are targeted for edge server applications, while the client modules support robust embedded computing.
Rugged Embedded Computing Solutions
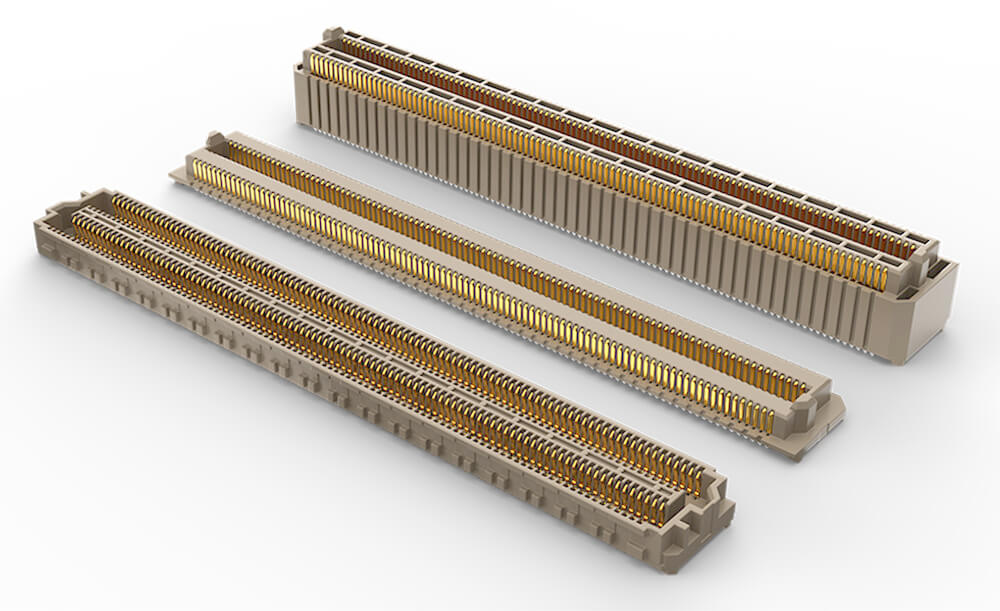
VITA 42 XMC is a widely deployed mezzanine standard used in high-reliability computers implementing switched-fabric architectures. XMC combines PCI Mezzanine Card (PMC) with serial fabric technology on proven mezzanine form-factors.
VITA 88 XMC+ connectors provide support for higher band rate, high-speed serial interfaces. Maximizing footprint compatibility, VITA 88.0 XMC+ supports the widely accepted XMC platform, while updating both electrical and mechanical characteristics in existing and future designs.
For more information or Samtec full suite of VITA solutions, please visit www.samtec.com/vita or email our technical experts at [email protected]


Leave a Reply